Some Types Of Vitamin B12 Supplements Can Cause This Side Effect – Health Digest
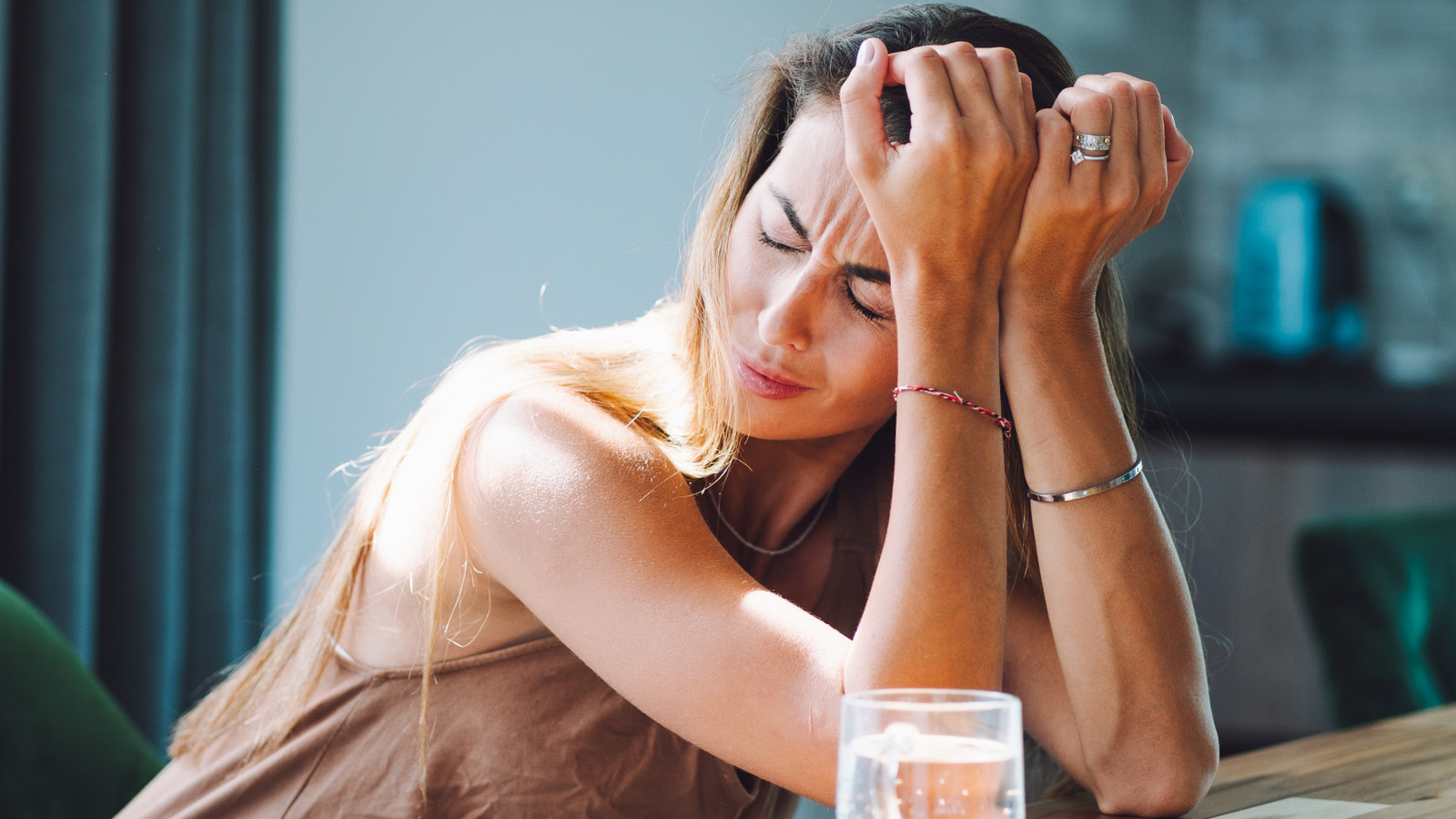
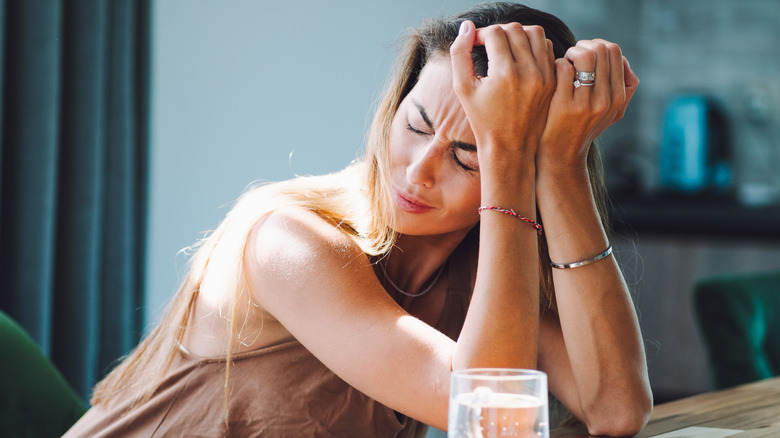
The eight B vitamins play important roles in converting the carbs, fats, and protein from your food into fuel. Not getting enough B vitamins can not only drain your energy but also prevent your body from making healthy blood cells. A deficiency in vitamin B12, in particular, can leave you feeling tired and weak due to a form of anemia.
While animal-based foods are naturally rich in vitamin B12, many plant-based foods and breakfast cereals are fortified to help people meet their needs. A vitamin B12 supplement is another option if you’re not getting the recommended 2.4 micrograms per day. Some supplements come in sweet-tasting gummies or liquid drops, which can make it easy to take more vitamin B12 than you actually need. The good news is, you don’t need to worry about overdosing on over-the-counter vitamin B12. Your body typically absorbs what it needs and gets rid of what it doesn’t use through your urine.
That said, some people have trouble absorbing vitamin B12 from food and oral supplements and may need it in injectable form. Injections can sometimes cause side effects like diarrhea, itching, dizziness, or nausea. And if you’re struggling with persistent headaches, too much vitamin B12 from injections might be a contributing factor.
Who’s at risk of a vitamin B12 deficiency
For the most part, people in the United States get plenty of vitamin B12 through their diets. Vegetarians and vegans may need to take an over-the-counter B12 supplement to ensure they’re getting enough, but people with vitamin B12 absorption issues may require prescription B12 injections. Older adults might also struggle to absorb enough B12, especially if they have reduced stomach acid, which is needed for proper absorption. Some people develop an autoimmune condition called pernicious anemia, which prevents the body from making a protein essential for absorbing vitamin B12. People with celiac disease or Crohn’s disease may also need B12 injections (per the National Institutes of Health).
If you’re low in vitamin B12 and receive an injection, your body might react to the sudden boost with a headache, nausea, or dizziness. These side effects usually go away fairly quickly. If you’re getting a B12 shot, be sure to stay hydrated and take a pain reliever if needed. Let your doctor know if you experience severe or persistent headaches (per Medicover Hospitals).
Do you need a vitamin B12 supplement?
You don’t need to worry if you fall short on vitamin B12 for a few days or even a few weeks. According to the National Institutes of Health, your body can store up to 2,000 times the amount of B12 you typically get in a day. That means your body can draw from these stores for years before you start to show signs of a deficiency. Unless you have a gastrointestinal condition that affects B12 absorption, it’s usually not an immediate concern. However, as you get older or if you drink heavily, it’s a good idea to keep an eye out for symptoms of low B12. An infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria can also lead to lower B12 levels.
Weakness and fatigue are common signs of a B12 deficiency, but they can also show up in many other conditions. If that weakness comes with weight loss, a poor appetite, or yellowish skin, it’s worth having your B12 levels checked by a doctor. Sometimes a deficiency causes neurological symptoms, such as numbness in the hands and feet, confusion, or trouble speaking or walking. Depression and irritability can also be warning signs of low vitamin B12 levels in your body.